This article focuses on examining how AI agents are applied in various industries, highlighting specific use cases where they enhance operations, automate repetitive tasks, and improve user interactions. The study is designed for a diverse audience, from business professionals to tech enthusiasts, offering practical insights on implementing AI agent technology in real-world scenarios.
1. Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping modern industries, and AI agents stand at the forefront of this transformation. These autonomous software systems have become essential tools that not only execute tasks but also learn, adapt, and optimize processes across diverse sectors. From revolutionizing classroom experiences through personalized learning to automating complex customer service interactions and refining manufacturing operations, AI agents offer unprecedented value. By combining advanced machine learning, natural language processing, and intelligent decision-making, they empower organizations with enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness.
This article, “AI Agents in Action: Real-World Applications Transforming Key Industries”, examines the myriad ways AI agents are utilized in practice. The discussion will cover specific industry use cases—including education, customer service, manufacturing, and finance—highlighting how practical implementations solve real-world challenges. We will also consider emerging trends, ethical issues, and the associated risks to provide a balanced analysis. Whether you are a business professional seeking ways to optimize operations or a tech enthusiast eager to understand modern innovations, this comprehensive guide offers detailed insights backed by recent research and industry examples.
2. AI Agents in Education
Education is undergoing a profound transformation as institutions worldwide harness the power of AI to create more personalized, efficient, and engaging learning experiences. AI agents in education are used to tailor educational content, evaluate student performance, and provide real-time tutoring and emotional support.
2.1 Personalized Learning and Adaptive Curriculum Development
AI agents are increasingly integrated into personalized learning platforms. These intelligent systems analyze students’ strengths, weaknesses, and progress to adjust lessons dynamically. For instance:
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: Technologies like Carnegie Learning’s MATHia analyze student performance data to customize lesson plans, ensuring each learner faces appropriate challenges.
- Automated Syllabus Creation: AI-driven tools can create personalized syllabi by incorporating the latest research and trends, enabling a curriculum that evolves with student needs.
AI agents in education also support self-directed learning. They monitor individual engagement levels and intervene proactively when a student shows signs of disengagement or struggle. By interpreting emotional cues through sentiment analysis, AI tutors can adjust their teaching methods in real time, providing a human-like interaction that enhances the learning experience.
2.2 Administrative Efficiency and Automated Assessments
The integration of AI agents in education dramatically reduces administrative burdens on educators. Notable applications include:
- Automated Grading and Assessment Tools: Programs like Gradescope reduce teacher workload by swiftly grading assignments and exams, allowing instructors to focus on more creative teaching activities.
- Curriculum Optimization through Data Analytics: AI systems provide insights that help educators identify at-risk students and tailor interventions accordingly, ensuring that teaching strategies are data informed.
Using these applications, educational institutions maintain high assessment quality and streamline routine processes. AI agents help by automating repetitive tasks while still preserving the quality and individuality of student feedback.
2.3 Virtual Tutors and Simulation-Based Learning
Beyond administrative tasks, AI-powered virtual tutors offer round-the-clock support to students. These tutors:
- Provide Personalized Feedback: They assess individual learning needs and dynamically adjust instructional content, ensuring that students remain engaged throughout the learning process.
- Facilitate Simulations and Gamified Learning: Initiatives like ‘PitchQuest’ create immersive, AI-generated simulations where students can practice real-life scenarios—for example, venture capital pitching simulations—that sharpen their practical skills.
Virtual tutors also make education accessible to diverse populations, thereby fostering inclusivity by overcoming geographical and physical barriers.
2.4 Summary of Key Educational Use Cases
Below is a table summarizing the primary applications of AI agents in education:
| Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Learning Platforms | Tailor content to individual learning styles using adaptive algorithms | Customized education, improved engagement |
| Automated Grading & Assessment | Utilize AI tools to grade assignments and provide real-time feedback | Reduced teacher workload, faster evaluations |
| Virtual Tutors & AI Assistants | Offer 24/7 support with AI-based instruction and personalized recommendations | Enhanced accessibility, continuous support |
| Adaptive Curriculum Development | Design and update curriculum using advanced data analytics | Up-to-date content, responsive to trends |
Table 1: Overview of AI Agent Applications in Education
The innovative use of AI in education not only personalizes the learning process but also makes it more efficient and accessible, paving the way for smarter educational systems that empower both students and instructors.
3. AI Agents in Customer Service
In the realm of customer service, AI agents are transforming the way companies interact with consumers by automating routine tasks, delivering prompt responses, and providing personalized service across multiple channels.
3.1 Enhancing Efficiency Through Automation
Customer service is a fast-paced environment where rapid response and precision are critical. AI agents excel in automating repetitive tasks, thus improving operational efficiency:
- Multi-Channel Support: AI-powered customer service solutions handle inquiries across SMS, email, chat, and social media, ensuring that customers receive timely responses regardless of the platform.
- Self-Service Solutions: According to recent studies, up to 61% of customers prefer using self-service options for simple issues, which AI agents efficiently handle while reducing response times.
By managing multiple interactions simultaneously, AI agents significantly enhance operational productivity and reduce costs for enterprises.
3.2 Intelligent Problem Resolution and Personalized Responses
AI agents have evolved beyond simple chatbots to become intelligent assistants that understand context and customer sentiment. They provide:
- Dynamic Troubleshooting and Technical Support: AI agents guide customers step-by-step through troubleshooting processes, reducing the incidence of escalated issues and ensuring accurate support.
- Personalized Service Experiences: These systems tailor responses based on historical data and real-time customer behavior, resulting in higher customer satisfaction scores (CSAT).
For example, Zendesk’s AI agents are pre-trained on vast amounts of customer service interactions, enabling them to resolve up to 80% of issues without human intervention. This personalized approach not only anticipates customer needs but also builds long-term trust and loyalty.
3.3 Intelligent Data Collection and Proactive Insights
Beyond direct interaction, AI agents in customer service play a crucial role in data collection and analysis:
- Sentiment and Trend Analysis: AI systems continuously monitor customer interactions to identify emerging trends and potential problems, thus enabling proactive responses.
- Integration with Backend Systems: By interfacing with CRMs and other enterprise tools, AI agents provide detailed insights that support decision making and strategic improvements.
These capabilities allow organizations to refine their customer service strategies based on data-driven insights, ultimately creating a more responsive service ecosystem.
3.4 Visualization: AI-Enhanced Customer Service Workflow
Below is a Mermaid flowchart outlining the process of an AI agent handling customer service tasks:
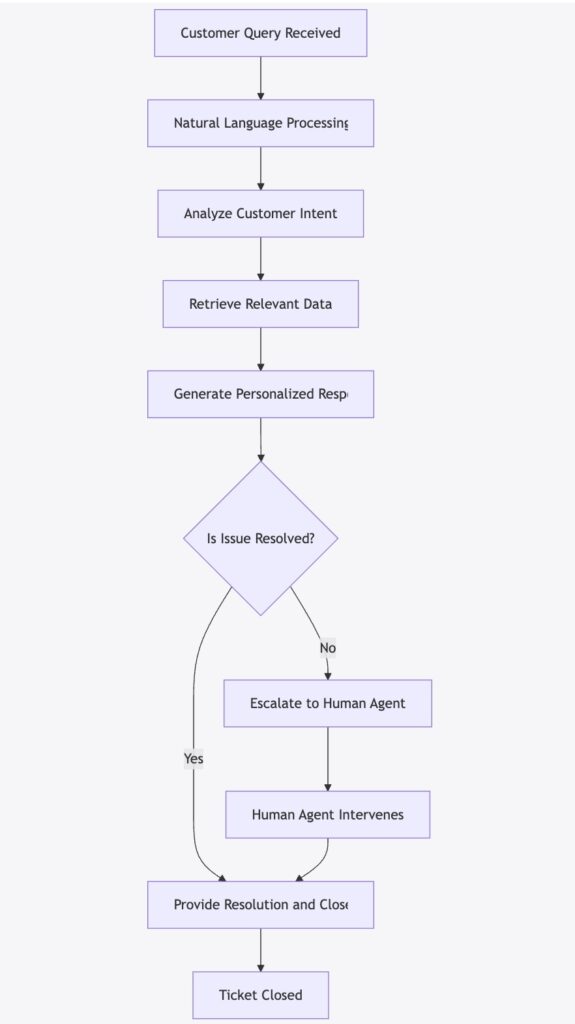
Figure 1: Flowchart Illustrating the AI-Enhanced Customer Service Process
3.5 Summary of Customer Service Use Cases
The table below outlines the key applications of AI agents in customer service:
| Use Case | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Channel Support | Handling inquiries across various platforms | 24/7 availability, reduced response times |
| Intelligent Troubleshooting | Guiding customers through step-by-step solutions | Faster resolutions, higher CSAT |
| Proactive Data Analysis | Monitoring interactions to identify trends and adjust strategies | Enhanced planning, cost reduction |
| Seamless CRM Integration | Connecting with backend systems for real-time data insights | Improved decision-making, personalized service |
Table 2: Overview of AI Agent Applications in Customer Service
By automating routine tasks and providing intelligent, personalized support, AI agents are redefining the customer service landscape and driving enhanced operational efficiency.
4. AI Agents in Manufacturing
Manufacturing is a sector where efficiency, precision, and real-time data analysis are paramount. AI agents offer solutions that streamline operations, reduce downtime, and optimize production processes, ultimately boosting productivity and quality.
4.1 Predictive Maintenance and Real-Time Equipment Monitoring
One of the most impactful applications of AI agents in manufacturing lies in predictive maintenance. These intelligent systems analyze vast amounts of sensor data to predict equipment failures before they occur.
- Forecasting Failures: By continuously monitoring machine performance data, AI agents can forecast potential breakdowns, facilitating timely maintenance and minimizing unplanned downtime.
- Reducing Maintenance Costs: Early detection of issues leads to cost-effective interventions, lowering overall maintenance expenses while extending equipment lifespan.
4.2 Quality Control and Defect Detection
Ensuring consistent product quality is critical in manufacturing. AI agents are used to inspect products and detect defects in real time:
- Automated Inspection Processes: Machine learning algorithms analyze visual and sensor data to identify defects early in the production process, thereby reducing waste and improving quality control.
- Building a Knowledge Base for Continuous Improvement: As AI agents learn from defect patterns, they build an extensive knowledge database that helps refine processes and prevent future errors.
4.3 Supply Chain and Inventory Optimization
Efficiently managing supply chains and inventory is another strong suit of AI agents in manufacturing:
- Optimizing Production Schedules: By taking into account demand forecasts, inventory levels, and machine availability, AI agents help plan production schedules that maximize productivity and resource utilization.
- Streamlining the Supply Chain: AI agents analyze procurement data to recommend optimal suppliers and distribution methods, reducing operational costs while ensuring timely delivery of materials.
4.4 Energy Management and Sustainability
Energy consumption is a major cost center in manufacturing. AI agents contribute significantly to sustainability efforts by monitoring and managing energy use:
- Real-Time Energy Monitoring: These systems continuously track energy consumption, identify wasteful patterns, and suggest actionable measures to reduce utility costs.
- Environmental Impact: Effective energy management reduces carbon footprints, aligning production processes with sustainability goals while lowering operational costs.
4.5 Visualization: Manufacturing Process Optimization
Below is a table summarizing the primary applications of AI agents in manufacturing:
| Use Case | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance | Analyzing equipment data to anticipate and prevent failures | Reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs |
| Quality Control | Automated defect detection through real-time data analysis | Improved product quality, reduced waste |
| Production Planning | Optimizing production schedules based on real-time data and forecasts | Increased productivity, efficient resource utilization |
| Supply Chain Optimization | Streamlining supplier selection and inventory management | Cost reduction, timely material availability |
| Energy Management | Monitoring and optimizing energy consumption | Reduced energy costs, enhanced sustainability |
Table 3: Overview of AI Agent Applications in Manufacturing
By integrating AI agents into manufacturing workflows, industries can achieve higher levels of efficiency, quality, and sustainability—a transformation that not only bolsters competitiveness but also supports innovation in production processes.
5. AI Agents in Finance
The financial sector has been rapidly transformed by AI agents, which are increasingly being deployed to manage risk, enhance decision-making, and improve customer experiences. Their ability to process vast datasets in real time makes them ideal for tasks that require precision and rapid adaptation.
5.1 Enhanced Risk Management and Fraud Detection
Financial institutions face the constant challenge of mitigating risk and detecting fraudulent activities. AI agents contribute substantially in these areas by:
- Real-Time Fraud Detection: Leveraging anomaly detection algorithms, AI agents analyze transaction data continuously, identifying inconsistencies that may indicate fraudulent behavior.
- Automated Compliance Checks: These intelligent tools assist in adhering to strict regulatory standards by automating routine compliance tasks and regulatory reporting, thereby reducing manual errors.
5.2 Personalized Financial Advisory and Robo-Advisors
AI agents are revolutionizing how financial services personalize customer interactions:
- Customized Recommendations: By analyzing individual financial behavior, AI agents provide tailored advice for investments, savings, and other financial decisions. This personalized approach is exemplified in services where AI agents function as virtual financial advisors.
- Adaptive Asset Management: Through continuous monitoring of market trends, AI agents adjust asset management strategies in real time, ensuring that portfolios remain aligned with risk profiles and market conditions.
5.3 Automation and Operational Efficiency
The automation capabilities of AI agents in finance extend beyond customer interaction to core operations:
- Document Processing and Data Retrieval: AI-powered systems help extract structured data from financial documents, thereby automating processes such as loan servicing and investment analyses.
- Workflow Optimization: By automating repetitive tasks like data entry and transaction processing, AI agents free up financial professionals to focus on strategic initiatives, driving overall efficiency.
5.4 Visualization: Financial Applications of AI Agents
Below is a table summarizing the core use cases of AI agents in the financial industry:
| Use Case | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fraud Detection and Risk Management | Real-time analysis of transactions to detect and prevent fraudulent activities | Enhanced security, reduced risk |
| Personalized Financial Advice | Customized investment recommendations and asset management | Improved customer satisfaction, better returns |
| Automated Compliance | Streamlined regulatory reporting and adherence to financial regulations | Reduced errors, cost savings |
| Document Processing and Data Analysis | Extraction and organization of data from financial documents | Faster processing, improved data accuracy |
Table 4: Overview of AI Agent Applications in Finance
By integrating these advanced solutions, the financial sector can achieve faster decision-making, enhance financial access, and reduce systemic risks—all while personalizing services to match individual customer needs.
6. Emerging Applications and Ethical Considerations
While industries like education, customer service, manufacturing, and finance lead the AI revolution, new applications continue to emerge, spurred by technological advances and evolving market needs. It is also important to address ethical concerns that come with increased AI adoption.
6.1 Emerging Applications in Healthcare and Beyond
Although not as extensively highlighted as other sectors, healthcare has also begun to see the benefits of AI agents:
- Advanced Diagnostics: AI agents assist in patient data analysis, helping to predict disease onset and guide personalized treatment plans.
- Medical Simulation and Training: Virtual AI tutors are used to simulate surgical procedures and offer real-time feedback to medical students, enhancing the quality of training.
Additionally, industries such as logistics, retail, and human resources are exploring AI agent technologies to streamline operations and improve decision making. Each industry leverages AI’s capacity to process real-time data and provide actionable insights tailored to specific operational needs.
6.2 Ethical Considerations and Challenges
As with any transformative technology, the widespread adoption of AI agents introduces several ethical challenges and regulatory concerns:
- Data Privacy and Security: Given the vast amounts of personal and sensitive data processed by AI agents, robust measures must be in place to protect privacy and comply with regulations such as GDPR and FERPA.
- Bias and Fairness: AI models trained on biased data can inadvertently reinforce inequalities. Regular audits, diverse datasets, and transparent algorithmic processes are essential to mitigate these issues.
- Human Displacement and Labor Dynamics: As AI agents take on roles traditionally performed by humans, concerns around job displacement and the need for upskilling become increasingly significant. Policymakers and industry leaders must work together to ensure a balanced integration of AI technologies while preserving the valuable human elements of work.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Ensuring AI agents operate within clear ethical guidelines is pivotal. Governance frameworks and oversight mechanisms must be updated to reflect the rapidly evolving technology landscape, balancing innovation with accountability.
6.3 Visualization: Ethical and Operational Challenges in AI Adoption
Below is a Mermaid flowchart that captures the key ethical and operational challenges associated with AI agent integration:
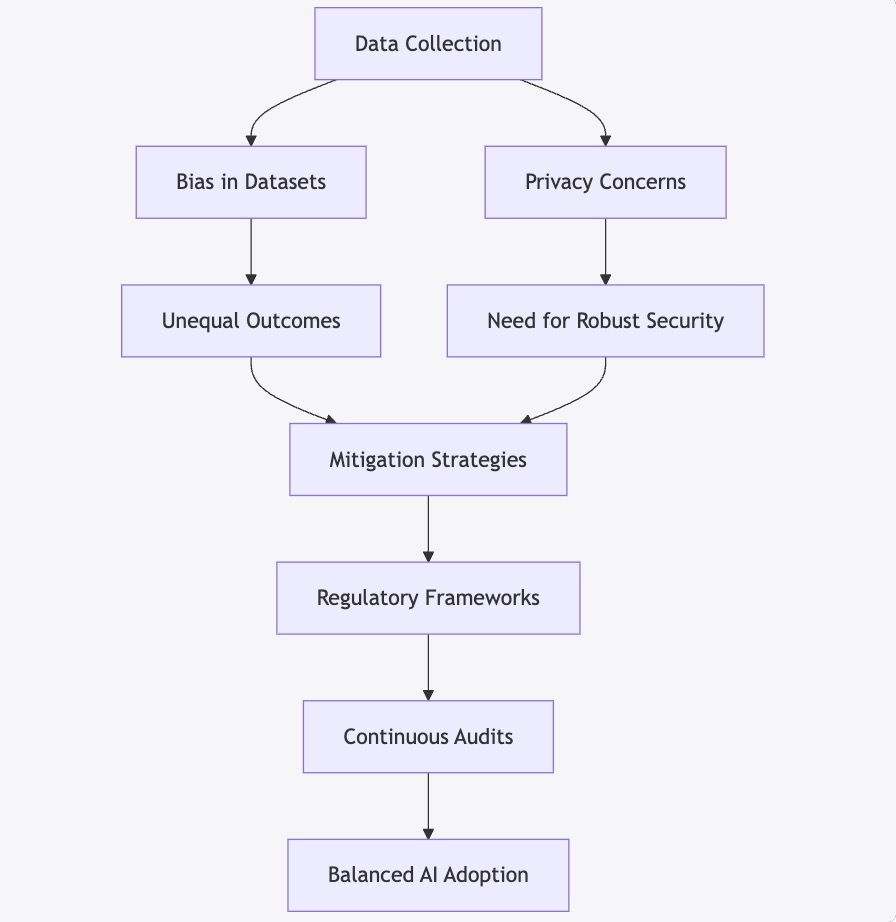
Figure 2: Flowchart Illustrating Key Ethical and Operational Challenges in AI Integration
The visualization emphasizes that while AI agents offer transformative benefits, their deployment must be carefully balanced with ethical strategies and regulatory measures to ensure fair, secure, and responsible innovation.
7. Conclusion
AI agents are transforming industries by providing unprecedented automation, personalization, and data-driven insights that boost efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and improve operational outcomes. The following key insights summarize the article:
- Education: AI agents enable personalized learning, automated assessment, and virtual tutoring, thereby creating adaptive and accessible educational environments.
- Customer Service: They enhance multi-channel support, streamline troubleshooting processes, and provide proactive insights, ultimately reducing response times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing: AI-driven predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization result in cost reduction, improved product quality, and enhanced sustainability.
- Finance: With applications in fraud detection, personalized advice, and operational automation, AI agents empower financial institutions to make faster, more accurate decisions while ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Emerging Applications and Ethics: While AI agents expand into healthcare and other sectors, addressing ethical challenges—including data privacy, bias, and workforce impacts—remains crucial for sustainable innovation.
Businesses, educators, and policymakers must embrace AI agents thoughtfully. By integrating these advanced digital systems, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation while ensuring that ethical considerations keep pace with technological advancements. As industries continue to evolve, the strategic deployment of AI agents will be the key to achieving long-term success and maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly digital world.
In conclusion, the journey toward comprehensive AI integration calls for a collaborative effort among technology developers, industry experts, and regulatory bodies. By fostering an ecosystem that values innovation alongside fairness and transparency, we can harness the transformative power of AI agents to build a smarter, more efficient future for all.
References Used:
https://medium.com/accredian/ai-agentic-ai-in-education-shaping-the-future-of-learning-1e46ce9be0c1
https://ai-analytics.wharton.upe
https://www.teachfloor.com/blog/ai-agents-in-education
https://global.fujitsu/en-global/insight/tl-aiagents-financial-industry-20250418
https://cloud.google.com/discover/finance-ai
https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/12/agentic-ai-financial-services-autonomy-efficiency-and-inclusion/
How to Build a Successful Strategy for Agentic AI in Manufacturing
https://www.performixbiz.com/blog/a-complete-guide-to-ai-agents-in-manufacturing
https://www.salesforce.com/service/ai/customer-service-agents/
AI Agents in Healthcare: Transforming Diagnosis and Treatment



 How Mobile Technology Is Transforming Sports Betting Experiences
How Mobile Technology Is Transforming Sports Betting Experiences




